Combating excessive noise levels in the room

The experience of using aspiration units in the grain industry shows that during the operation of the equipment there is a high level of noise load in the working premises. High noise level negatively affects the operating personnel, which leads to a decrease in the quality of work and the occurrence of occupational diseases. Creation of dedusting systems devoid of these problems is limited, on the one hand, by the imperfection of existing equipment, and on the other hand, by the lack of devices and methods of effective control of noise parameters.
Modern aspiration systems, both centralized and local, provide for the presence of equipment that creates a vacuum in the system. The main such equipment are fans, which by their design and specificity of operation are the main source of noise in aspiration networks. Modern fans have a design that generates minimal noise (below the maximum permissible value of 80 dB) and practically does not create vibrations, but such fans are much more expensive than domestic analogs. In today's market conditions, it is more cost-effective to buy a domestic fan and equip it with vibration supports and silencer than to buy expensive imported equipment.
In this article we will consider the formation of noise in aspiration networks and ways to suppress it. As is known, fan noise consists of aerodynamic and mechanical components. Aerodynamic noise is caused by pressure pulsations and velocities of air flow in the flowing part of the fan and in the adjacent ducts. Mechanical noise is caused by the operation of the motor, bearings, etc. This noise has a wide range of frequencies, multiples of the fan speed, as well as frequencies of shock excitation of mechanical vibrations of structural parts.
Aerodynamic noise in ducts is mainly generated when the air flow passes through sharp edges, dampers, narrowed sections, guide vanes in rectangular ducts, etc. Any sharp edge or obstacle in the path of air flow creates turbulence and noise.
To assess the noise level in the premises, the entire frequency range is divided into separate bands - octaves. The geometric mean frequencies of the octave bands, at which noise regulation is carried out, are strictly standardized: 63, 125, 250, 500, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 and 8000 Hz. Noise is considered acceptable if the sound pressure levels measured with a noise meter or theoretically determined sound pressure levels in all octave bands of the standardized frequency range (31.5-8000 Hz) do not exceed the normative values. Noise standardization shall be conducted in accordance with the requirements of DBN B.1.1-31:2013 "Noise Protection".
When eliminating excessive noise load, the following problems arise: unknown characteristics of the sound source, which makes it difficult to calculate the necessary parameters of silencers; difficulty in determining the method of noise absorption (soundproofing of the equipment enclosure or installation of silencers); lack of a line of appropriate equipment. In modern fans the main component of noise is aerodynamic noise, respectively, the main way to reduce its intensity is the installation of silencers.
Silencers: types and application
Silencers are designed to reduce aerodynamic noise generated by fans and other equipment, as well as noise arising in the elements of air ducts. They are used in environments that do not contain explosive and radioactive impurities.
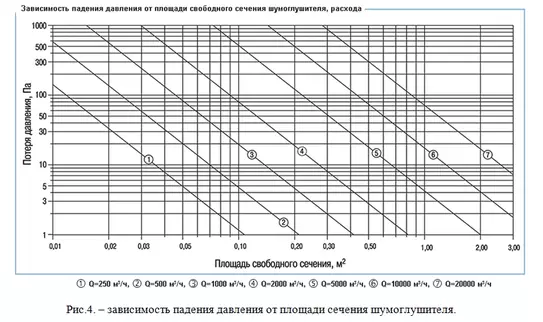
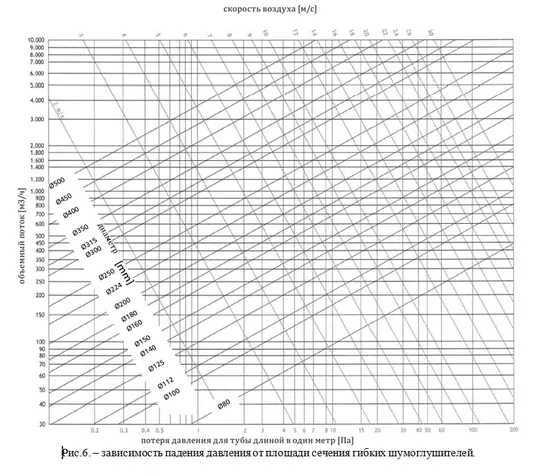
Silencers should be installed on the air discharge section, on its straight part, because the presence of any branches and resistances leads to the appearance of noise in the system. For effective operation of sound attenuators it is necessary to observe certain velocity regimes of air flows (the velocity should be up to 12 m/s). These requirements are the same for different types of silencers.
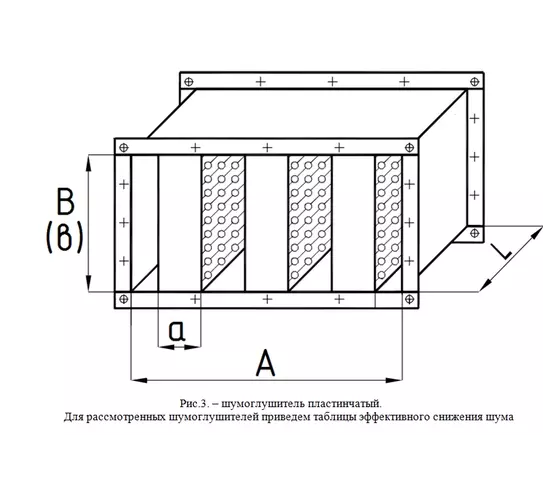
There are different types of silencers: round, rectangular, plate silencers, both domestic and imported. Let's consider domestic mufflers separately for each type.
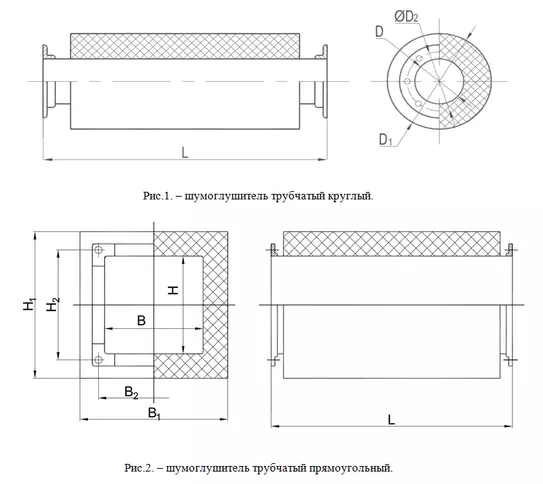
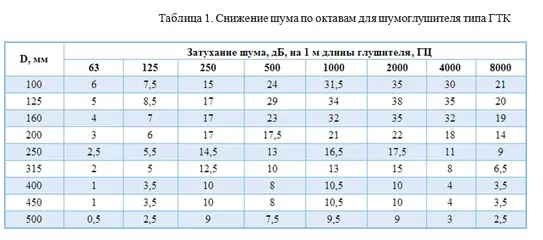
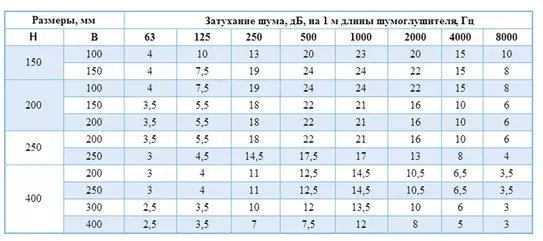
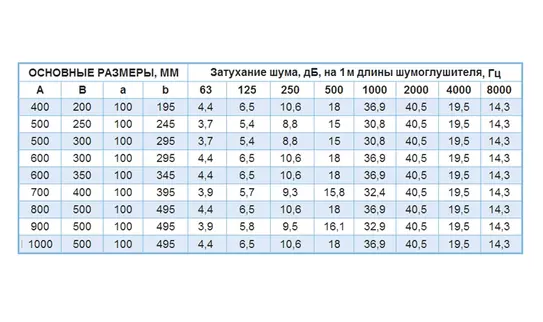
Round and rectangular silencers are similar both structurally and in principle of operation and differ only in geometric shape. These silencers are labeled GTC and GTP respectively.
Tubular silencers of round (GTC) and rectangular (GTP) cross-section are made of galvanized steel sheet and are used for the cross-sectional area of the duct up to 500x500 mm.
Tubular silencers consist of a casing and an inner perforated frame covered with fiberglass cloth. The space between the casing and the frame is uniformly filled with sound absorbing material.
Flexible silencers: an innovative solution
In order to eliminate the disadvantages of traditional silencers, Grain Capital Research and Production Complex in cooperation with Odessa National Technological University has developed a line of flexible silencers based on the experience of foreign manufacturers.
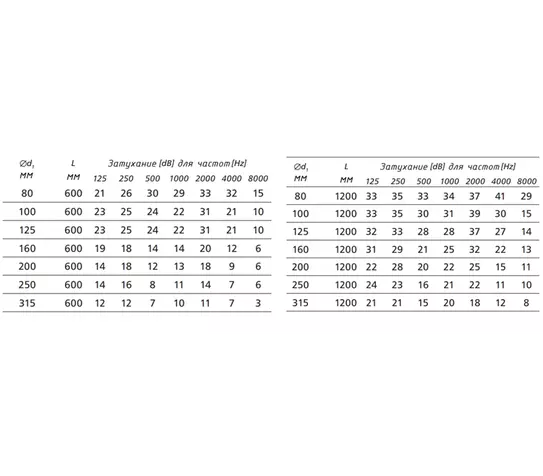
Flexible sound attenuator is a microperforated duct, wrapped with a polyester film preventing glass wool particles from getting inside the duct, a 25 mm thick layer of thermal insulation and an outer protective shell of multilayer aluminum foil reinforced with spiral steel wire.
Flexible silencers are used in ventilation and aspiration networks and have a high level of damping of sound vibrations, small size and low resistance compared to traditional silencers. The line of silencers developed by ONTU and Grain Capital meets the criterion: minimum size at maximum efficiency. It was created specifically for grain storage and processing companies.
The main difference between flexible silencers and traditional silencers is the flexible design of the housing, which allows them to be installed under compressed conditions. This design is ensured by the absence of a rigid frame; the sound absorbing material is attached to a flexible wire frame and lined with aluminum foil.

Advantages of flexible silencers
- Small size and weight.
- Low resistance.
- High sound attenuation efficiency.
The development of these silencers was made possible thanks to the standardization of sound source parameters (filter equipment fans) and acoustic measurements for each type of fan. The use of the new type of silencers has reduced their size and resistance compared to standard models, resulting in lower energy and material costs for the aspiration network.
This article considers ways of creating comfortable levels of noise pressure for personnel in rooms with aspiration equipment. The main method is the elimination of aerodynamic noise with the help of special equipment - mufflers. Their types and comparative characteristics in terms of noise reduction efficiency are presented.
Literature
DBN V.1.1-31:2013. Protection against noise.
Gusev, V. P.; Leshko, M. Yu. P., Leshko M. Yu. Acoustic and aerodynamic characteristics of flexible air ducts // AVOK. 2004. № 1.
Design of protection against noise and vibration of engineering equipment in residential and public buildings. Manual to MGSN 2.04-97.
Noise control in production. Reference book / Edited by Yudin E. Ya. Я. M.: Mashinostroenie, 1985.
Author:
Gaponyuk A.I., Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Odessa National Technological University, Odessa, Ukraine















